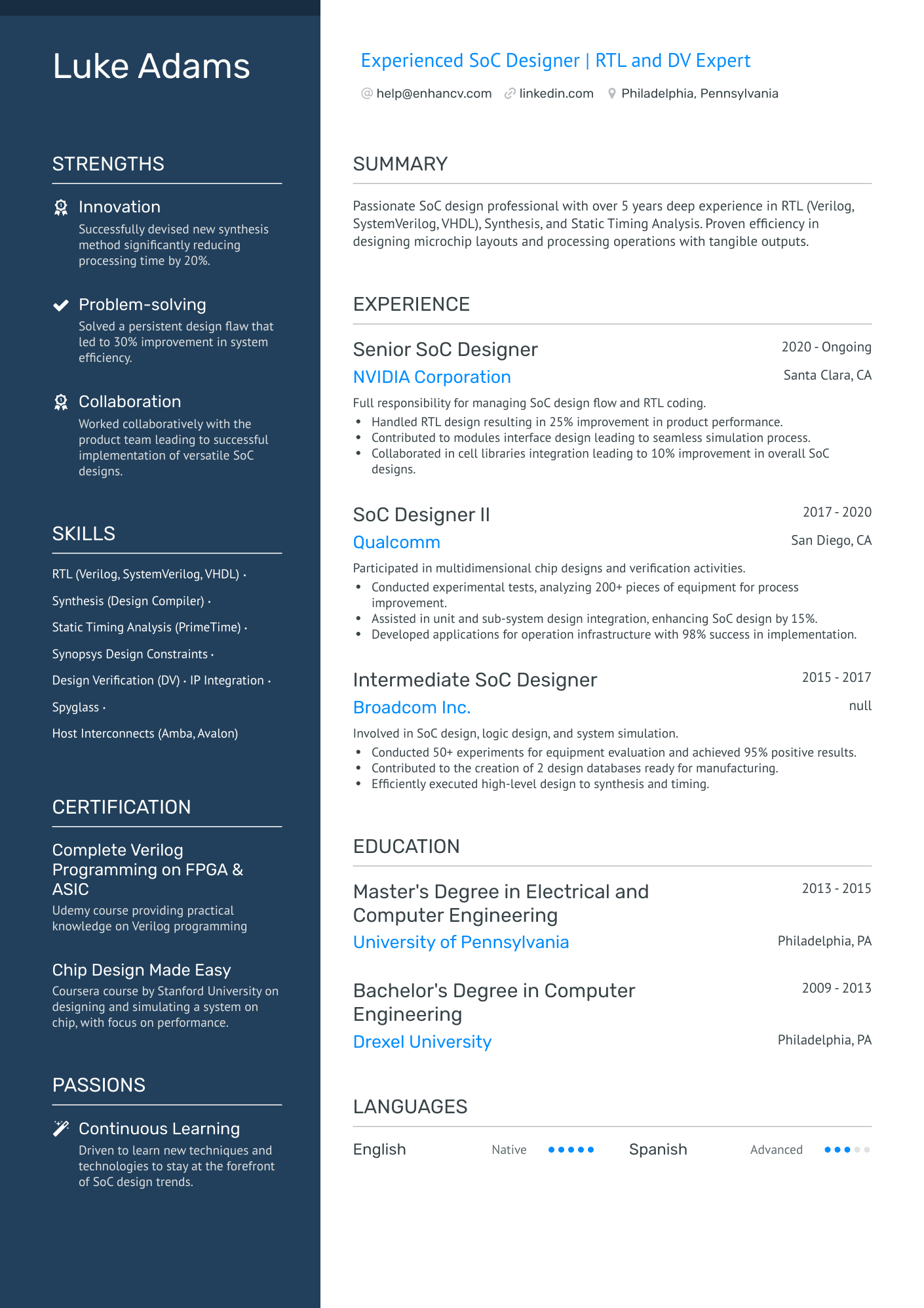
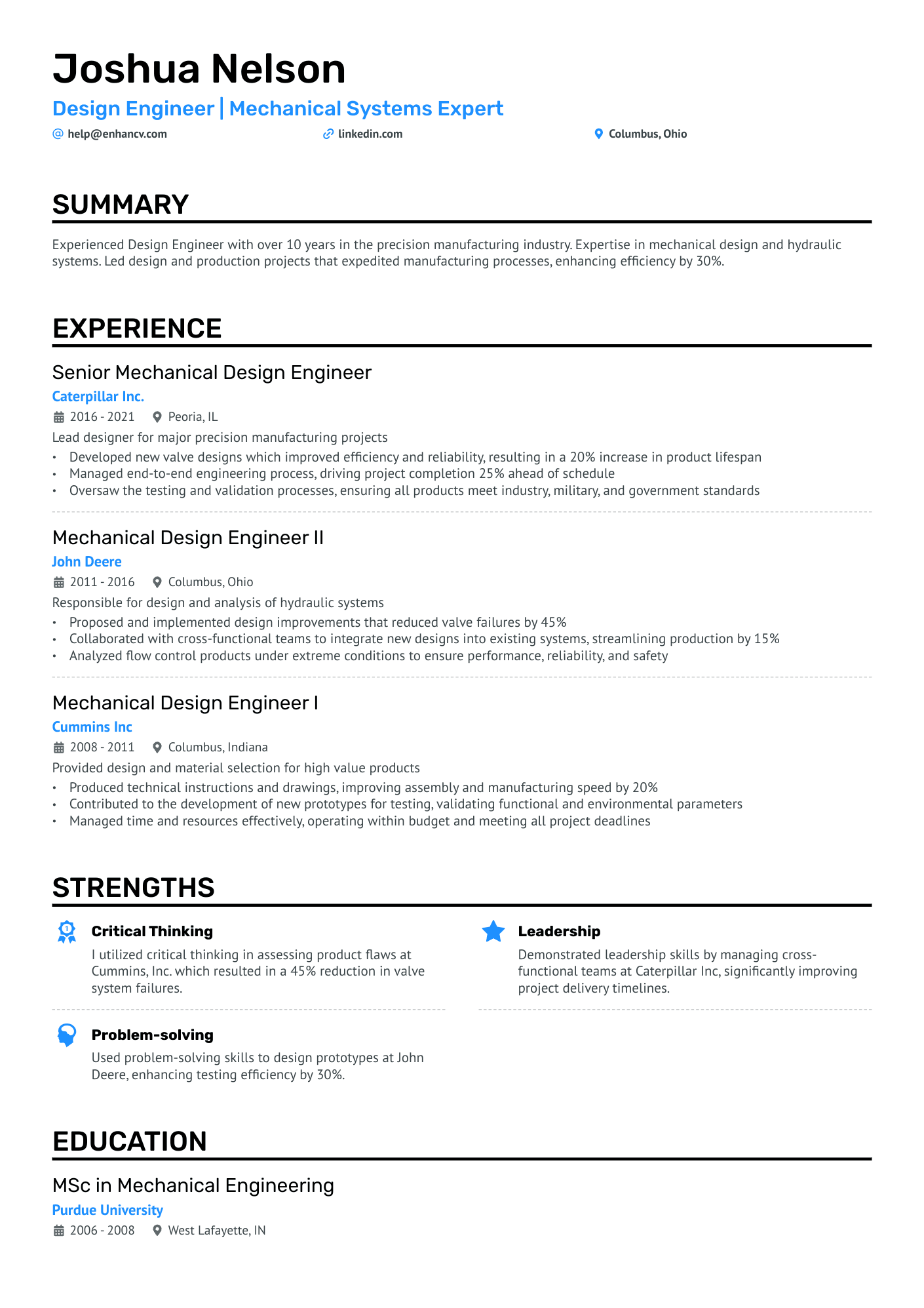
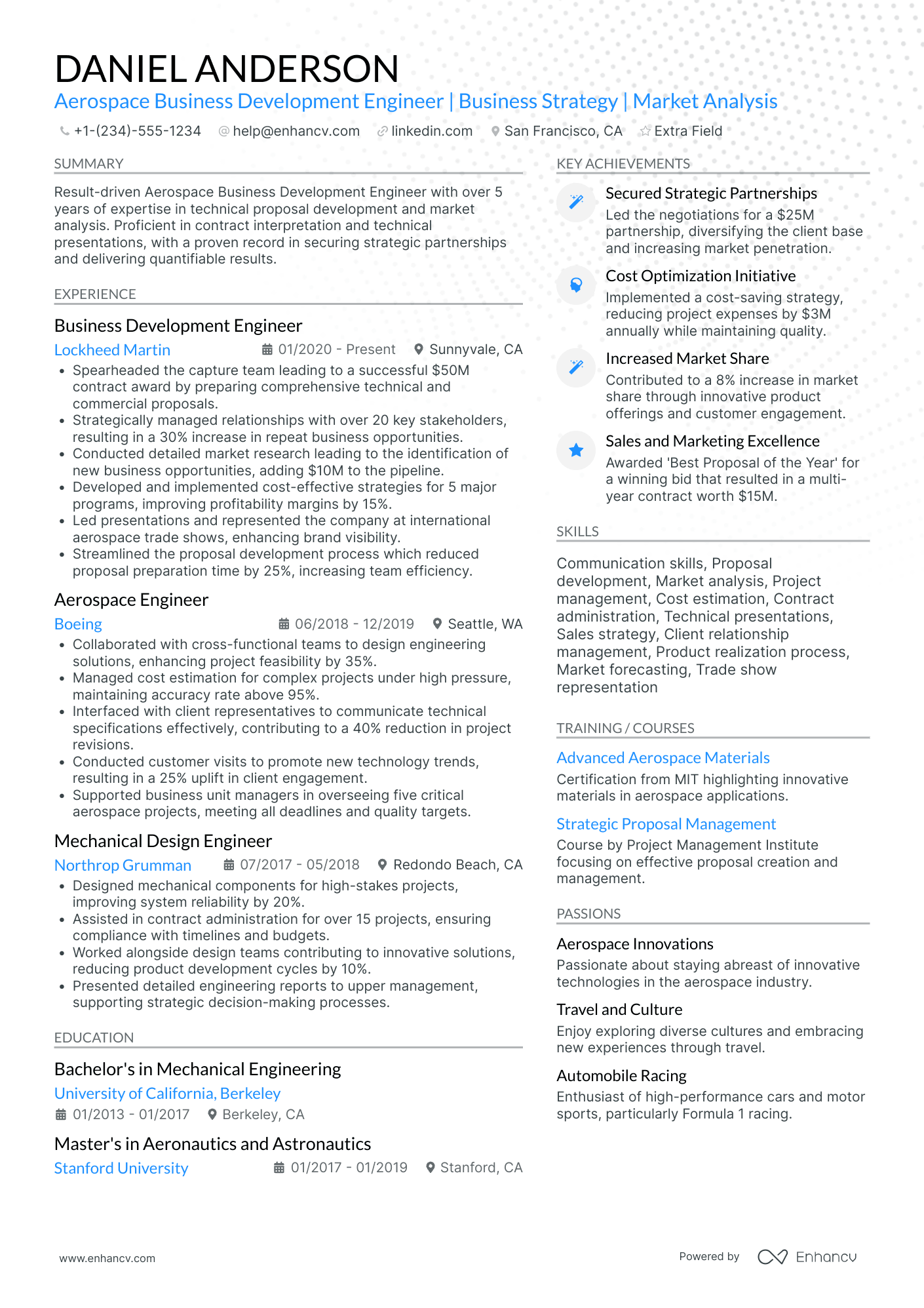
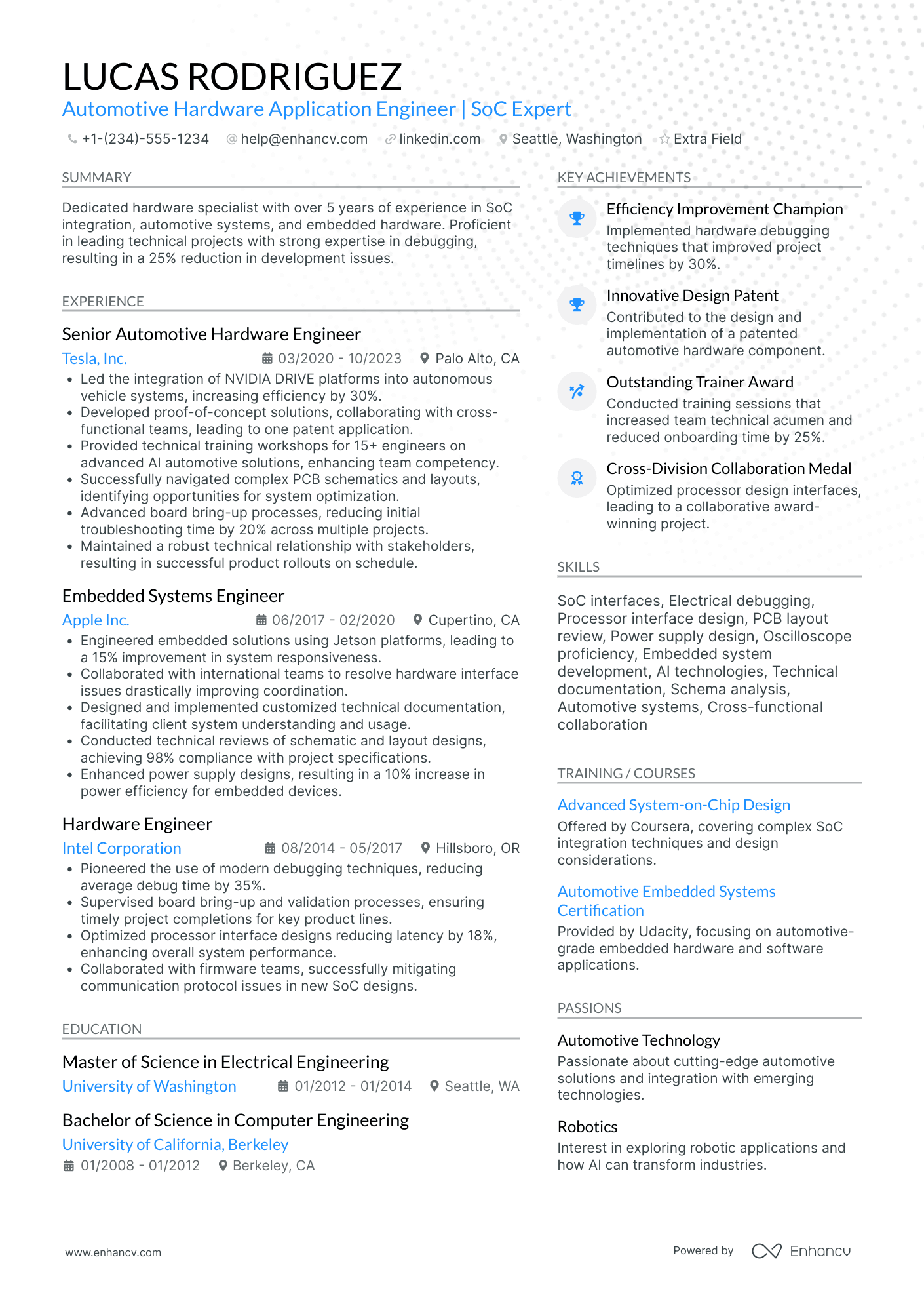
Meet Jason.
He’s the founder of the leading engineering firm in your city. He’s on the hunt for a new design engineer to join his team.
Jason’s firm has an impressive list of prestigious clients, and many of his former projects have gone on to win awards.
Joining his team as a design engineer would skyrocket your career.
But first you need to craft the perfect resume to impress the hiring manager.
You may have all of the qualities they’re looking for, but you must show them off in a way that makes you stand out from the other candidates.
We’re here to help you win that interview.
In this guide, we’re going to walk you through how to write a design engineer resume that will land you your dream job.
Let’s get started.
Our Design Engineer Resume Guide Will Teach You:
- The best format for a design engineer resume that shows of your background
- How to prove your past design success with real numbers
- 8+ ways to highlight your duties as a design engineer
- 20+ example technical and soft skills that prove you have what it takes to excel
Looking for related resumes?
Top Tips for Writing a Design Engineer Resume
With the right mix of experience, education and skills, you’ll be a successful design engineer working on outstanding products.
You need to display these three key qualities in your resume, or else you won’t get hired in the first place.
Companies want to make sure they’re hiring the right design engineer since the job is so important. The products you design will directly impact many people.
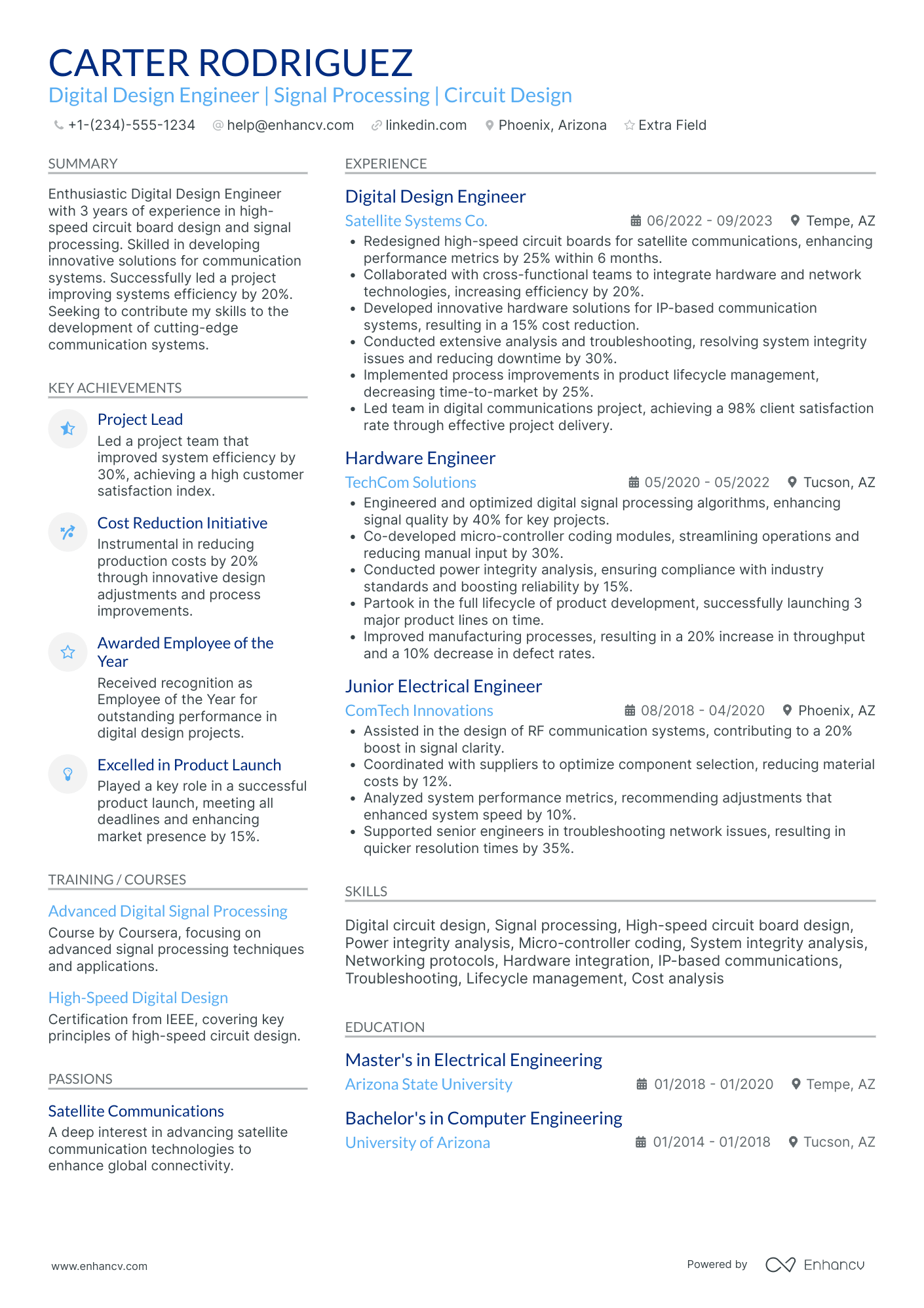
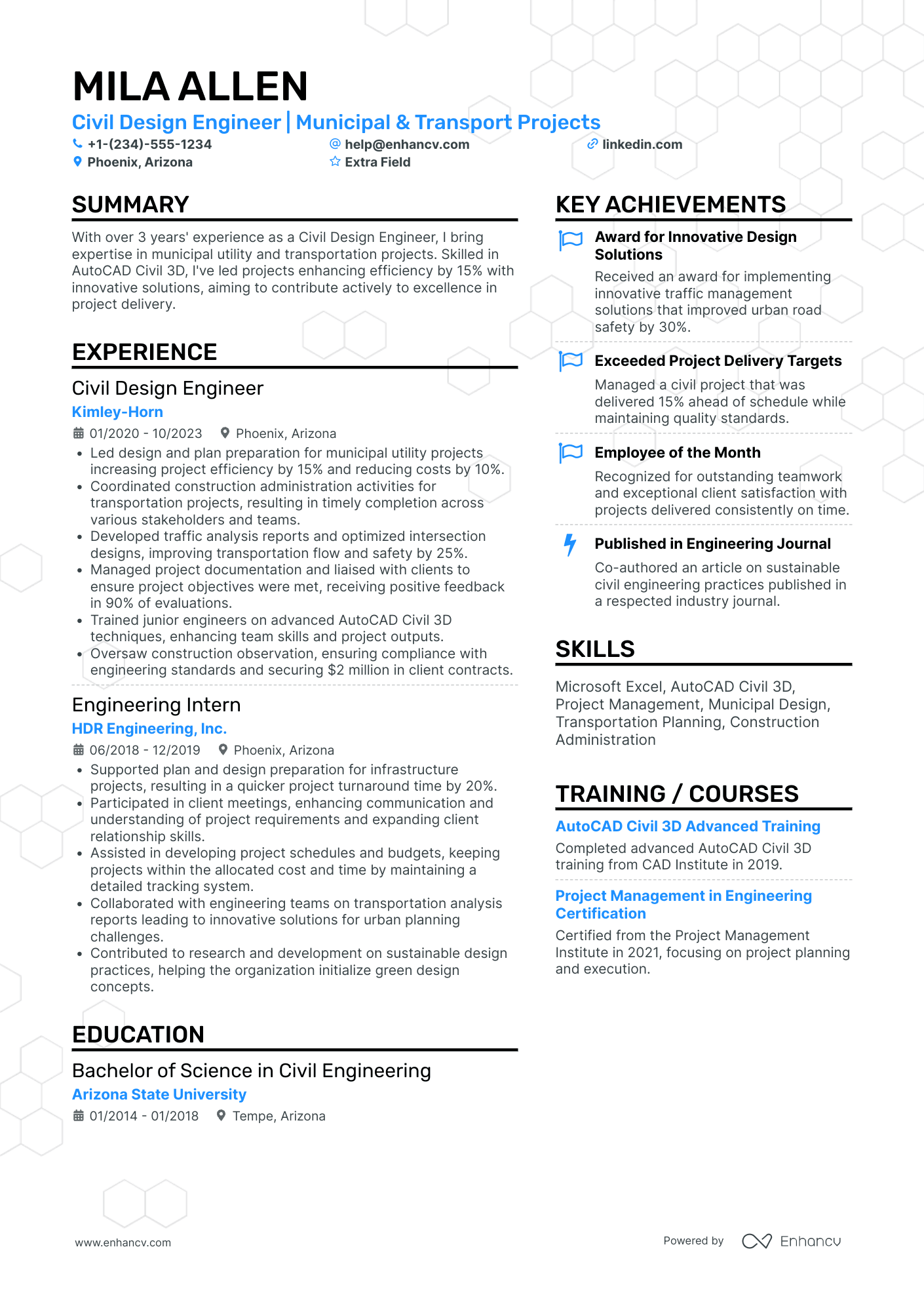
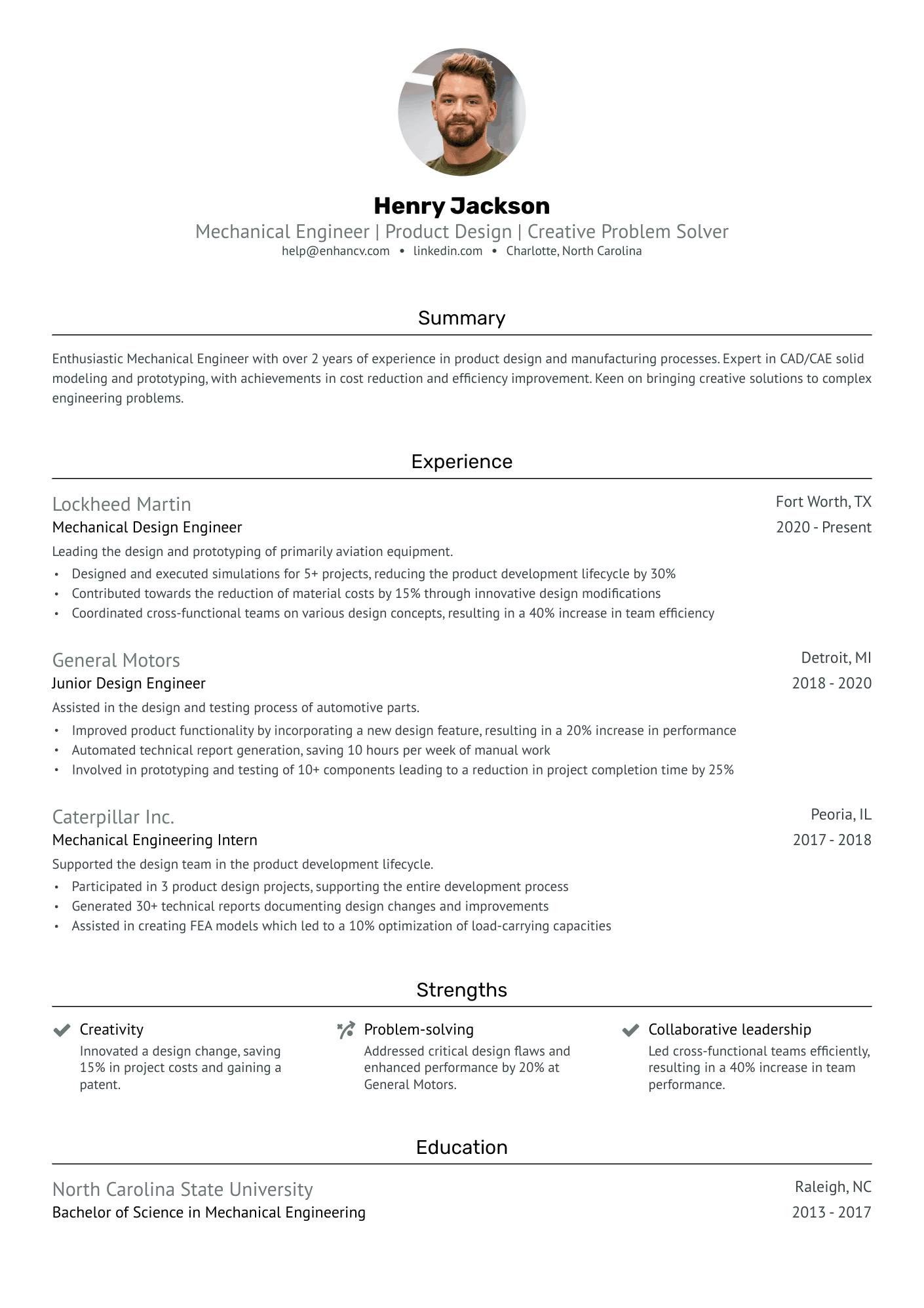
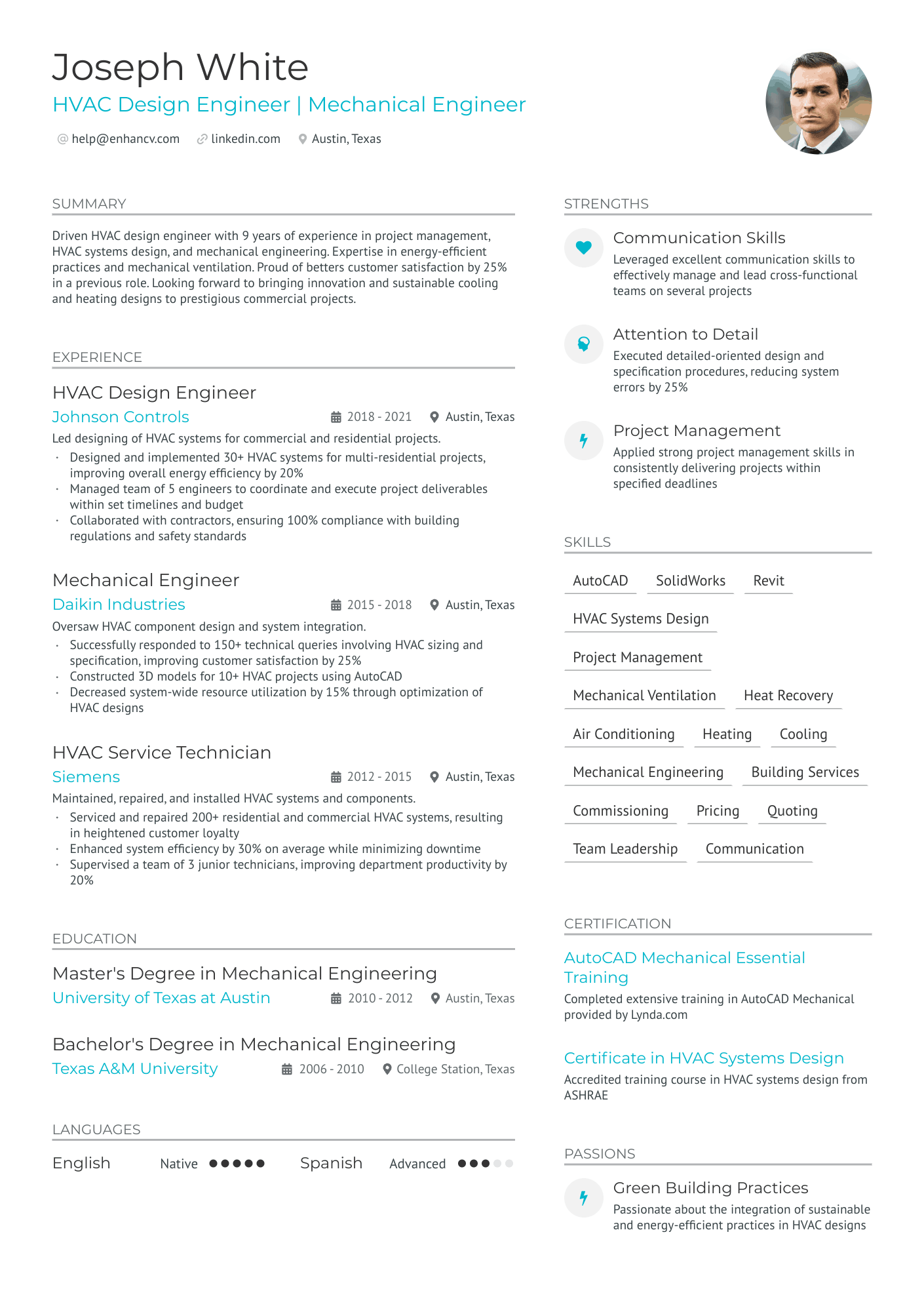
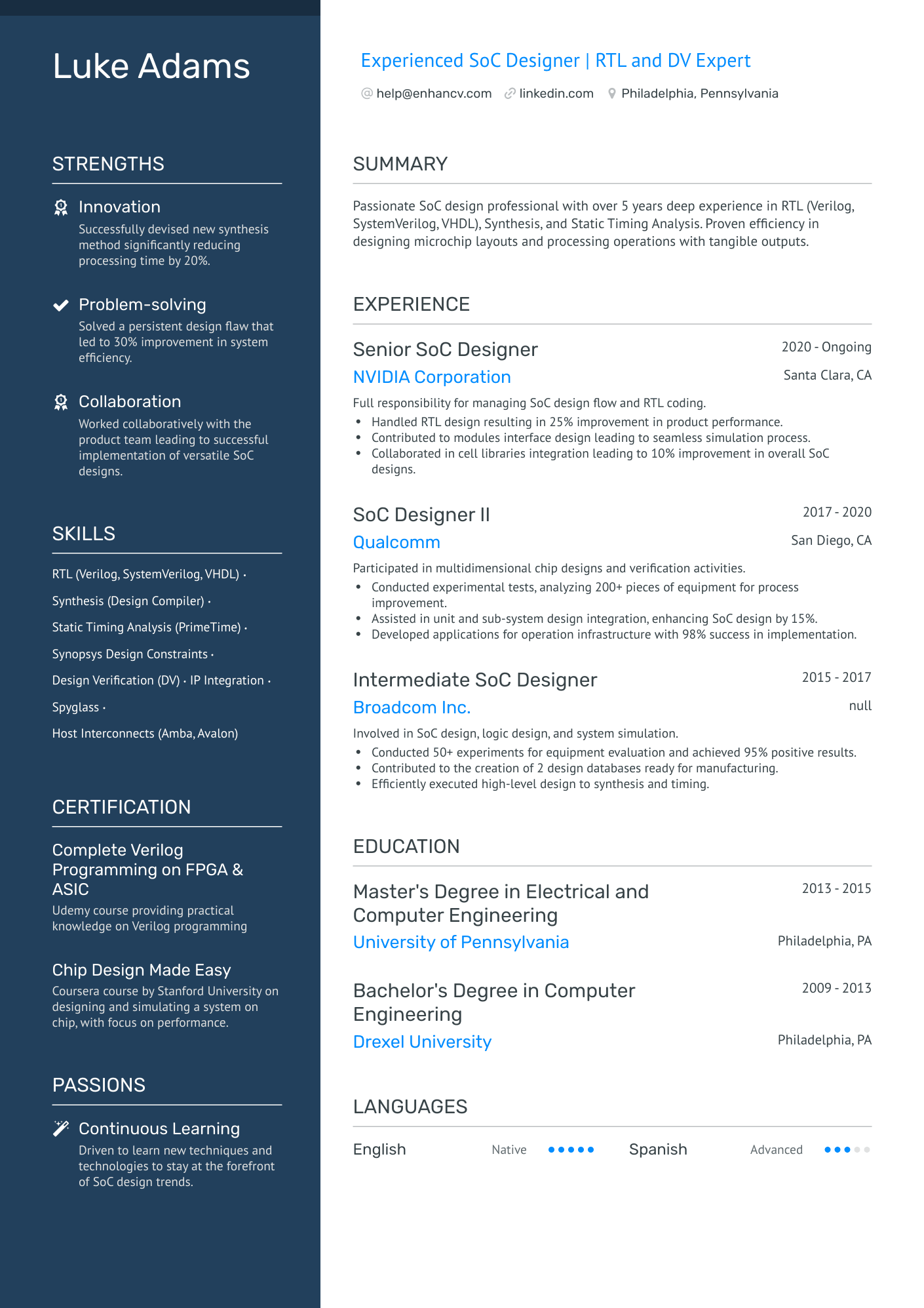
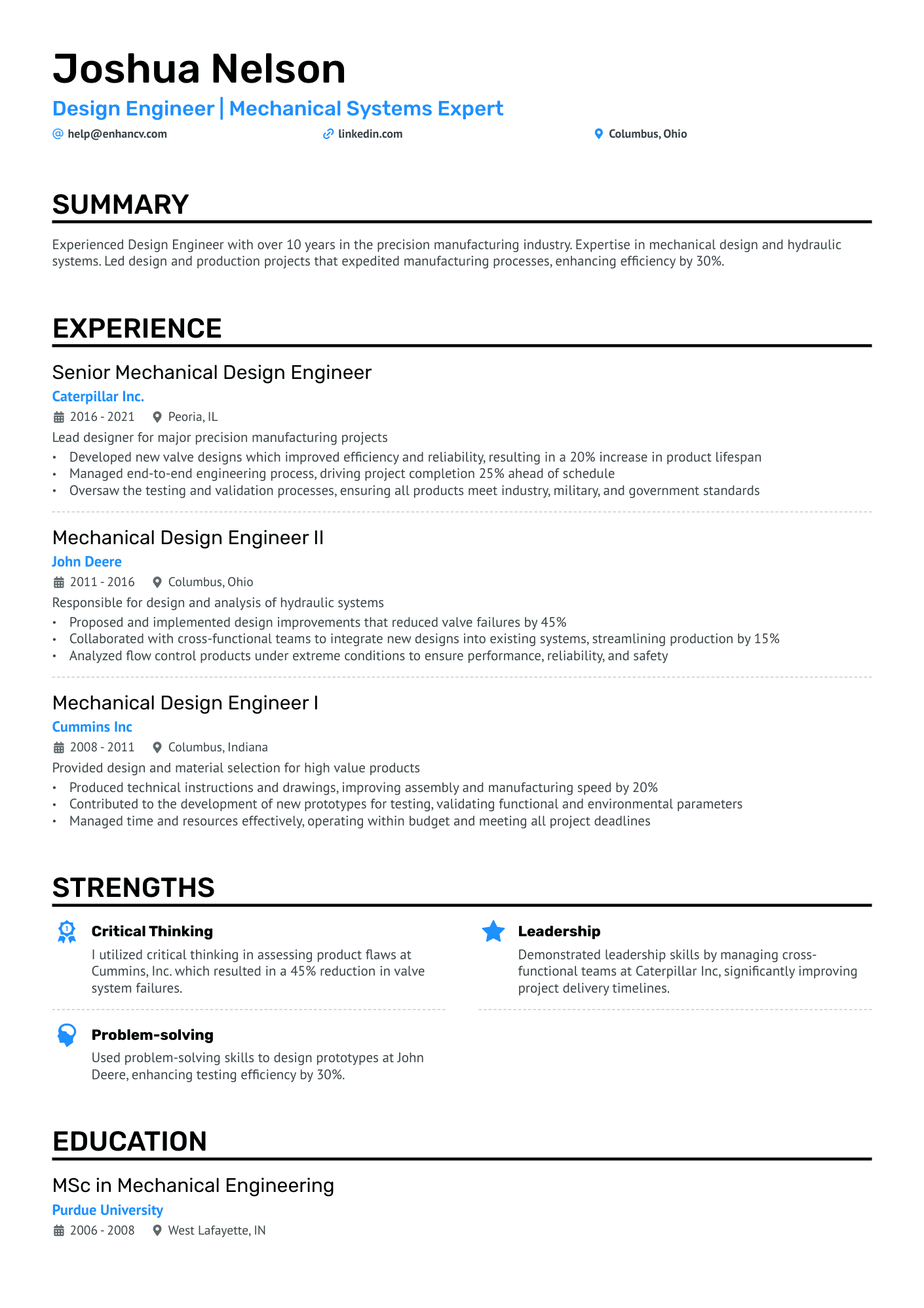
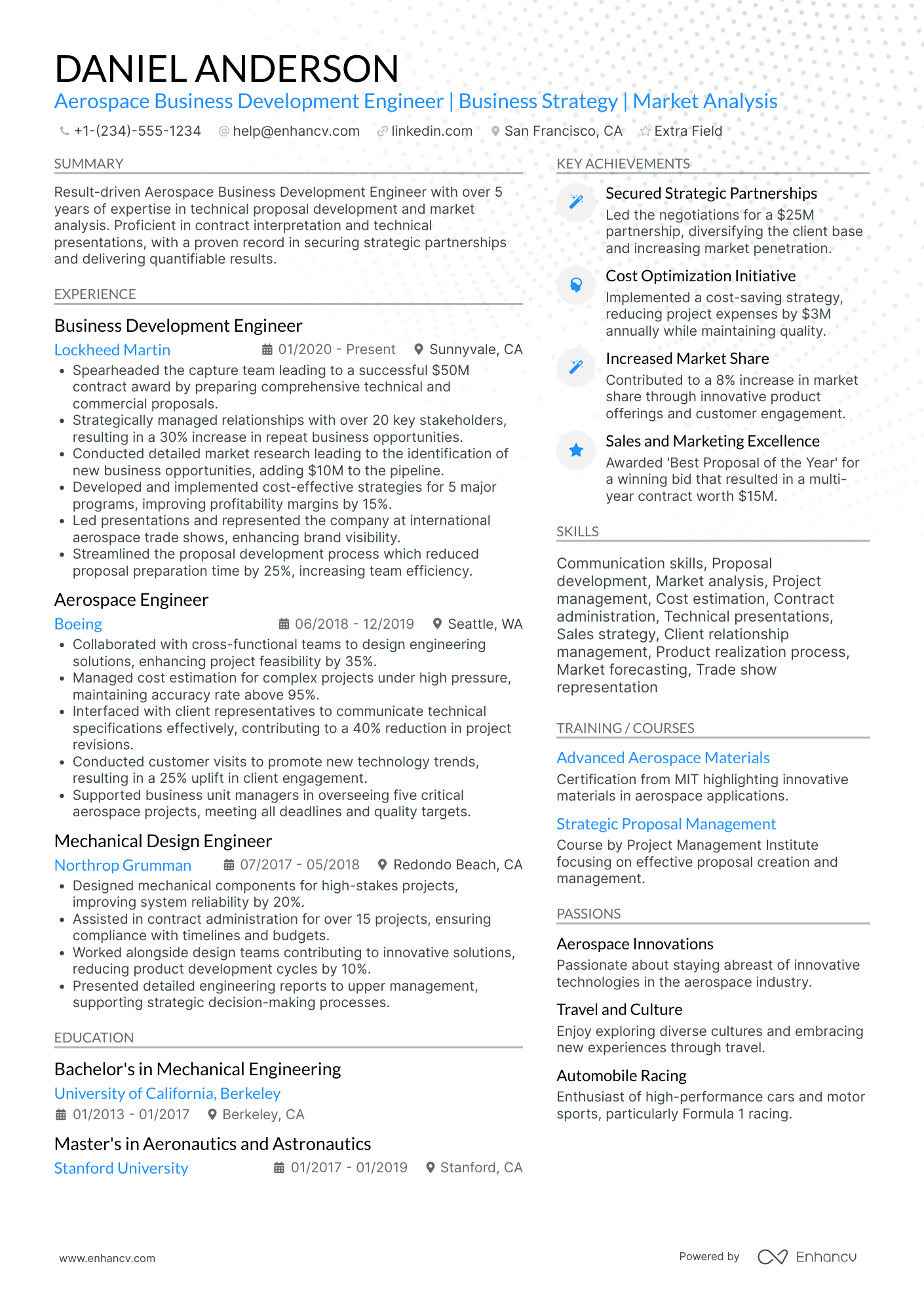
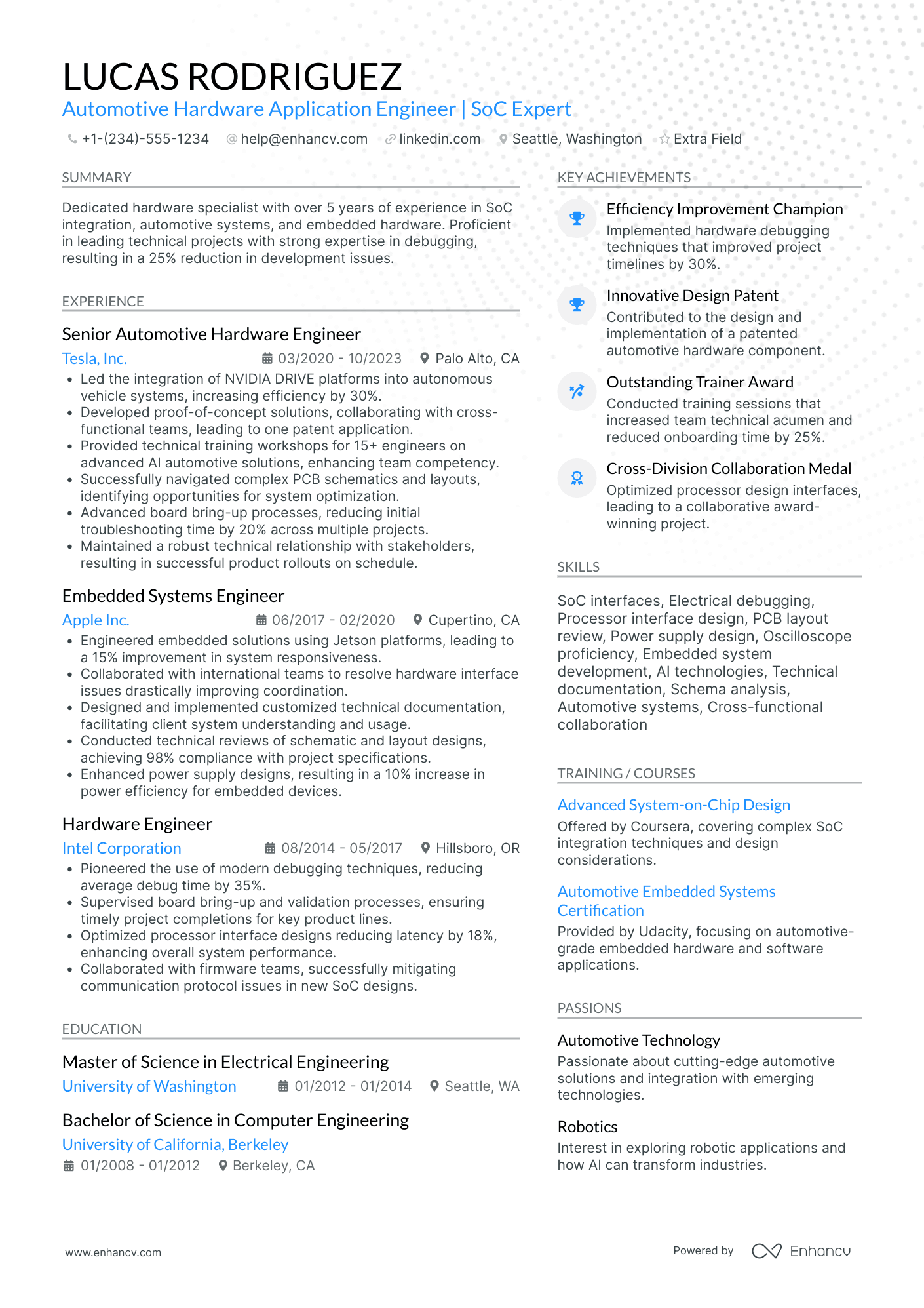
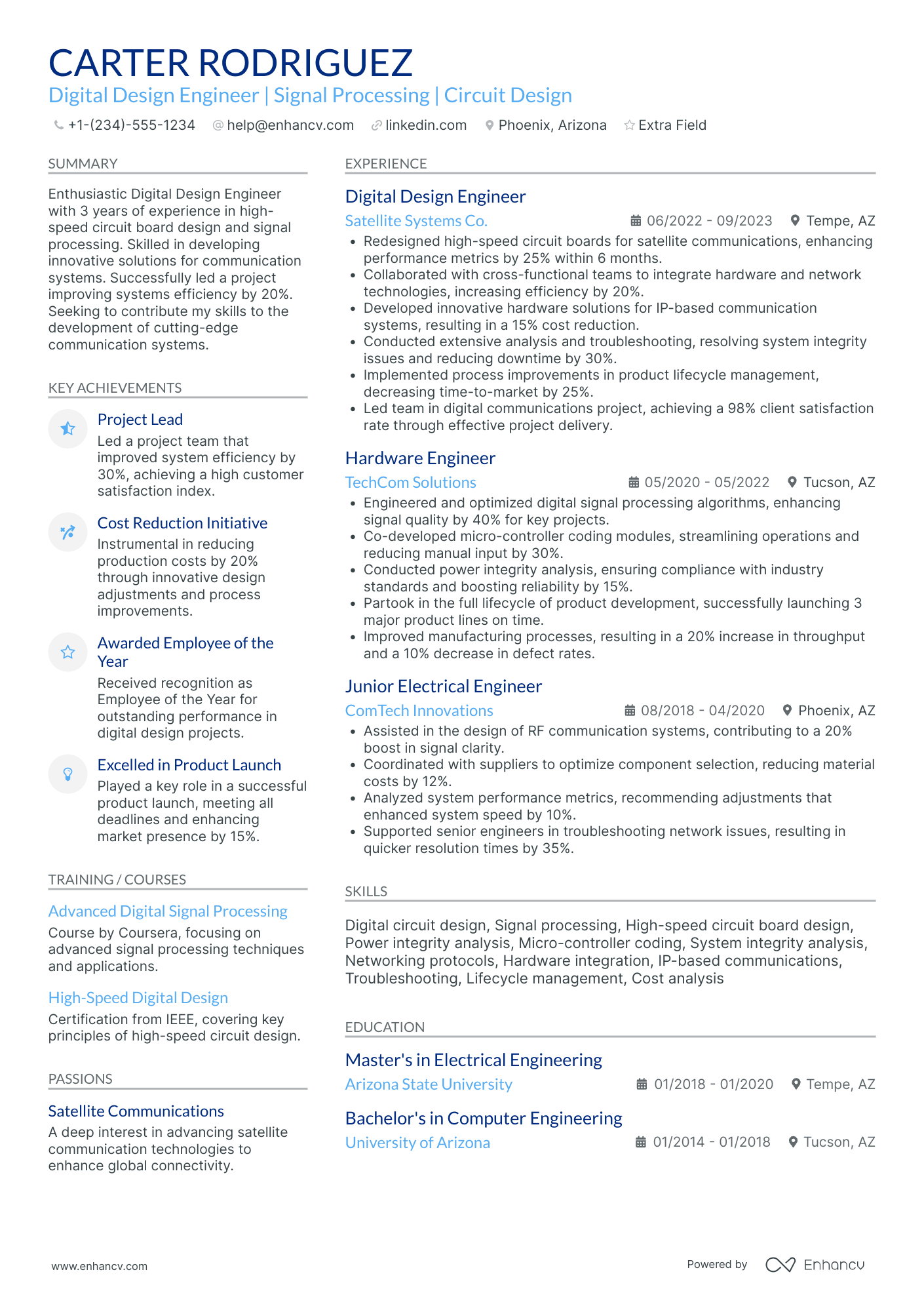
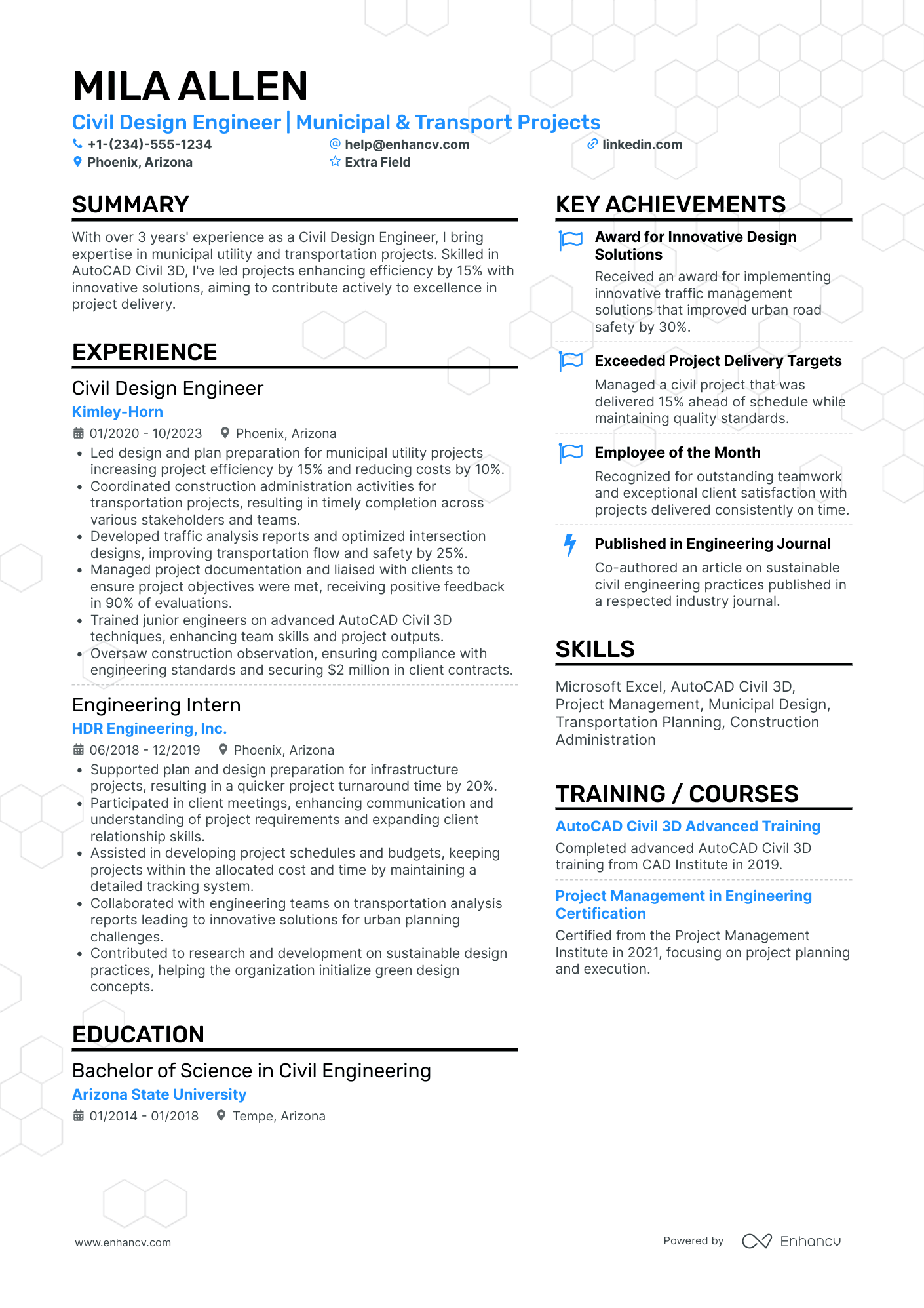
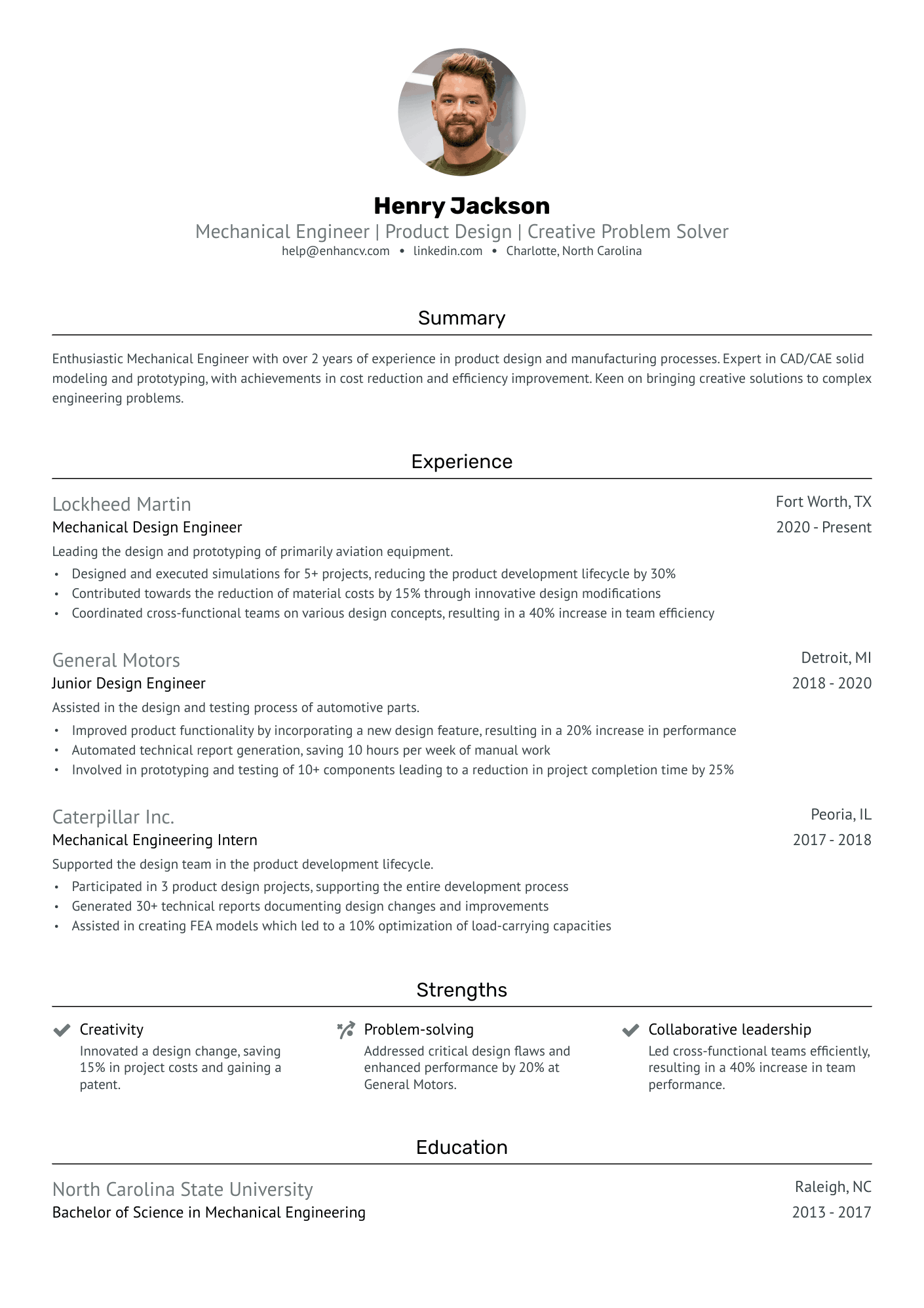
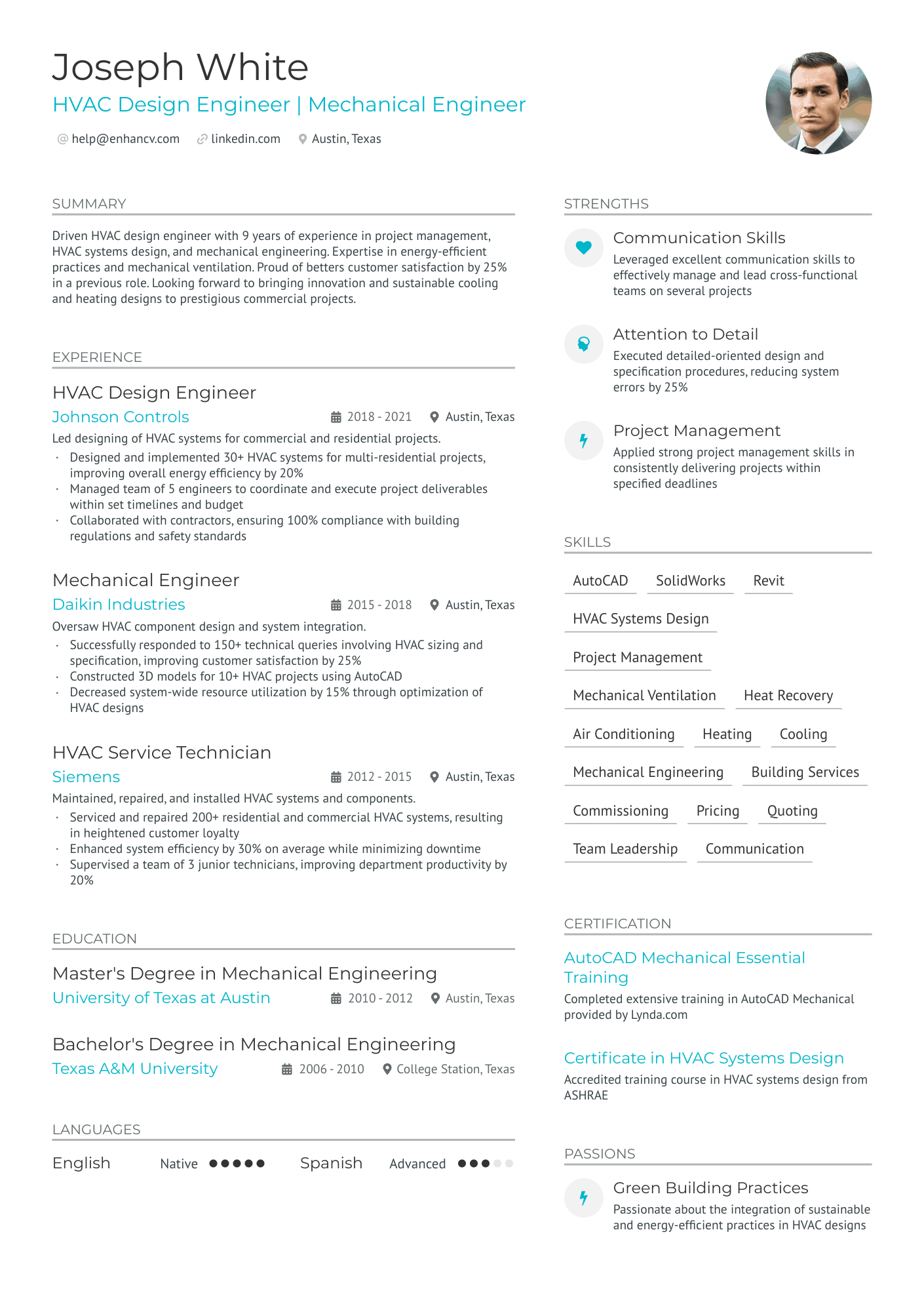
You can highlight your excellency best with a reverse chronological resume format.
This resume format emphasizes your experience first - the most trusted way to prove your knowledge in design engineering.
The reverse chronological resume also lets you:
- Talk about your education & qualifications
- Show your chartered engineering status (if you have it)
- Highlight your interest in the specific job you’re applying for
Here's what a recruiter will look for in your resume
- Have you designed and engineered functional products? What were they?
- Do you have a Bachelor’s or Master’s degree in a relevant engineering discipline?
- Have you solved design engineering problems in the past that have produced positive results?
- What industries are you most familiar with?
Answering these questions clearly in your resume will help the hiring manager decide whether or not they’ll read further. It all starts with an informative resume header.
Start by Writing an Informative Header for Your Design Engineer Resume
Your resume header is the first impression the hiring manager will have of you.
While it may seem like a basic resume section that doesn’t need any thought, putting in the extra effort makes an impact.
Let’s say you’re applying to an engineering firm.
Your may start with a header that looks like this:
Think about the market’s preferences – a Canadian resume, for instance, could have a different layout.
This header isn’t necessarily bad, but it’s very basic.
It lists the essential information about you: name, location, title and contact information. It doesn’t go above and beyond.
You can improve your header by adding extra elements such as:
- A title that describes your seniority level
- Your LinkedIn profile URL
This header checks all the boxes because it covers the essentials, but goes above and beyond by listing the seniority level of the candidate (Jr. Design engineer), and displaying a LinkedIn profile URL for the recruiter to look up.
Quantitative data is key on a design engineer resume
Most candidates simply list their job responsibilities on their resume. Stand-out candidates prove their past success with quantitative data.
Not sure where to start?
Ask yourself these questions:
- How many clients did you work with? What was the size of their budgets?
- Did you optimize products to improve efficiency? Use percentages to make your point.
- Do you have any publications or patents? How many?
This data belongs in your resume summary and experience section. Let’s talk about those now.
How to Write a Strong Design Engineer Professional Summary
Your design engineer resume summary should complete two goals:
- Prove to the hiring manager that you’re dedicated to landing that specific job role
- Show you have the experience, qualifications & skills necessary to excel
Mirroring the keywords used in the job posting will show the hiring manager that you’ve done your research and that you’re genuinely interested in working for their company. Plus, it will make your resume ATS friendly. (Applicant Tracking Systems)
Summarizing your level of experience, skill-level and educational background in a concise way will make the hiring manager want to read more.
Here are two examples of a design engineer professional summary. The first one needs a bit of work, and we’ll tell you why. The second summary is a strong example you should follow.
This summary won’t land the candidate an interview. Why not?
- It’s vague and generic. The summary isn’t personalized to the specific job posting.
- It says nothing about their skill-level, experience-level and past success as a design engineer.
Here’s an example of an excellent design engineer summary:
This summary has it all! It has detailed information about the candidate’s experience, highlighting both their technical and soft skills.
Optimize your resume summary and objective for ATS
Drop your resume here or choose a file.
PDF & DOCX only. Max 2MB file size.
Writing About Your Design Engineering Experience
The experience section of your resume should accomplish two things:
- Prove you’ve been successful as a design engineer before
- Show you have the right mix of technical and soft skills needed for the role
Before you write anything in the experience section, take a look at the job posting and review the responsibilities of the role, and the skills that they value most importantly.
This will help you narrow your focus about what you should mention when summarizing your past experience.
As a design engineer, your knowledge of design software will be important to the recruiter.
Note down how and when you have used software, such as AutoCAD, to complete your work.
Since you’ve already noted down key points from the job posting, you should know what software programs are necessary to know for the role.
List them directly within the experience section. Not only will this help your resume get picked up by applicant tracking systems, but it will tell the hiring manager exactly what they want to know.
Aside from your software and technical knowledge, having strong soft skills, and mentioning them in relation to your former roles, is essential to getting hired.
A huge part of the job as a design engineer is to work as a team, present your findings, and liaise with clients.
Proving to the hiring manager that you have the necessary collaboration and communication skills to do those things will make a great impression.
We’ll talk more about that later in this guide.
To get you started on writing your experience section, we found two examples of design engineer resumes for you - one is not so great, and the other is strong.
2 design engineer resume experience samples
- •Used computer tools to design products
- •Created prototypes and tested them
- •Improved efficiency of existing products
- •Presented designs to clients
This example may look fine at first glance, but there’s huge room for improvement. It only lists the responsibilities of their former role.
It doesn’t give the hiring manager any confidence that the candidate was actually successful in their former role, and can be trusted to be hired for this new one.
Here’s an example that will win over any hiring manager.
- •Developed and tested 100+ functional prototypes
- •Wrote technical documents to highlight improvements and findings to clients
- •Facilitated projects using AutoCAD, Catia V5, and Enovia
- •Analysed 300+ existing designs to maintain quality control, and minimized costs by an average of 30%.
This is an excellent example of an Experience blurb done well.
It includes quantitative data to show the candidate’s positive impact in their former role, building trust with the hiring manager, making them more likely to progress forward.
How to describe the duties of a design engineer on a resume
Here are some examples of design engineer responsibilities you can pick and choose from to add to your resume:
- Developed prototypes for testing
- Created technical reports to summarize findings
- Carried out quality control procedures to identify performance problems
- Improved functioning and efficiency of existing products with re-designs
- Presented designs and observations to clients
- Lead training sessions on design across other departments
- Kept up to date with the latest industry trends
- Maintained health and safety standards
How Should You Display Your Design Engineer Education?
The education section of your design engineer resume is one of the most important, since hiring managers want to ensure you’re fully qualified for the role.
It’s essential to highlight your education and qualifications in the best way possible, beginning with talking about your degree.
The most common university degrees for design engineers include:
- Product Design
- Mechanical Engineering
- Product design engineering Technology
- Engineering Manufacturing
Most companies will require a Bachelor’s, or even a Master’s degree to be considered for a job.
In some unusual circumstances, you may get hired without any formal education, if the company offers apprenticeships and training programs.
How to Include Certifications on Your Design Engineer Resume
While resume certifications can’t replace a university degree, having them can set you apart from other candidates. It’s important to remember that:
- Not all certificates are industry-wide approved
- Real experience is a better indication of performance
Here are some popular certifications for design engineering:
- Autodesk ACU & ACP Certifications
- MathWorks MAT Lab Certification Program
- CATIA Certification
- SOLIDWORKS Certification
What Skills Are Most Important for a Design Engineer Resume?
Hiring managers want to see that you have the right mix of technical and soft skills in your resume skill section.
You should be familiar with design programs such as AutoCAD and Enovia. Check the job role description to see which programs the company favours.
Soft skills are often forgotten in resumes, especially in engineering roles. Candidates mistakenly think that their technical background is all that matters, but as a design engineer, you need a strong set of soft skills to get ahead.
You’ll need to present your designs, provide an explanation for your findings, analyze results, and communicate with your team, clients and your boss.
Here are a list of skills you can include in your design engineer resume.
15 technical skills to include on a design engineer resume
- CAD Packages: Solidworks, Pro Engineer, AutoCAD
- Enovia
- Rendering packages: Hypershot, V-Ray
- Creating 3D models
- Developing and implementing design standards
- MATLAB
- CATIA
- Analysis: ANSYS, Fluent, Hyperview
- Windchill PDMLink
- Pro/INTRALINK
- Solid & Parametric Modeling
- Geometric Dimensioning & Tolerancing
- Design for Manufacturability (DFM)
- ISO 9001 Standards
- Excel
8 soft skills to include on a design engineer resume
- Presentation skills
- Project management
- Communication skills (written & spoken)
- Writing technical documentation
- Team collaboration
- Client liaison
- Budget management
- Mathematical and analytical skills
Summary: What Are the Top Tips for the Best Design Engineer Resume?
- Include quantitative data in your resume to show your past success in design
- Use the same keywords that are in the job posting in your resume sections
- List the software programs you’re most familiar with using, such as AutoCAD
- Highlight your mix of technical and soft skills to show you’re a well-rounded design engineer
Design Engineer resume examples
By Experience
By Role